
- Home /
- Products /
- Cartographie
Cartographie
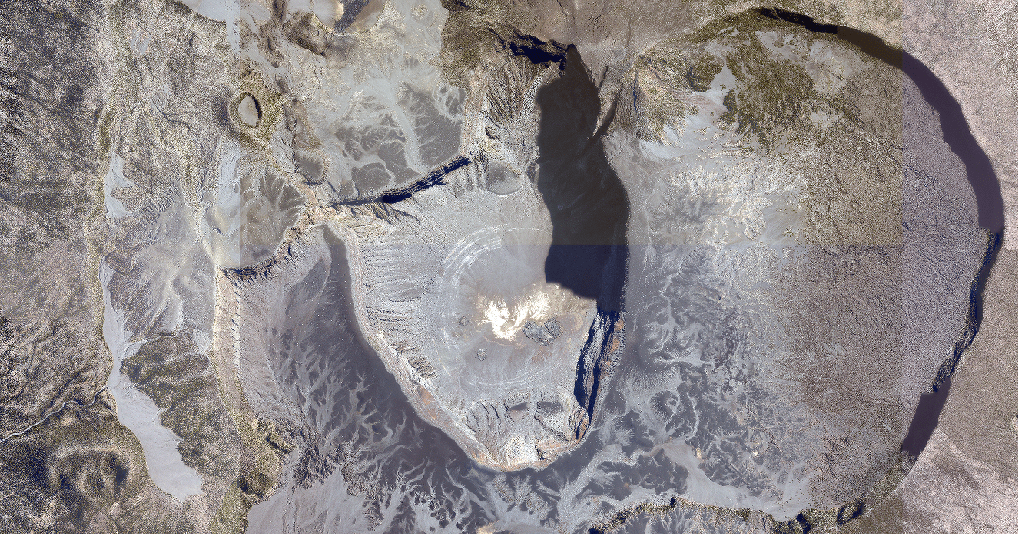
Mont Karthala
Choungou Chahalé & Choungou Cha Gnoumeni
GEOLOGICAL MAPPING
Located in the Indian Ocean, the Comoros archipelago consists of four islands of volcanic origin (Grande-Comore, Anjouan, Moheli and Mayotte) which appeared during the Tertiary and Quaternary periods.
The soil and subsoil resources of this archipelago are very little studied. The few studies that have been carried out show a geological context characterized by very diverse magmatic rocks ranging from the basaltic facies found in all the islands to the trachytes of Mayotte and the phonolites present in Mohéli, Anjouan and Mayotte (Lacroix, 1922). Any prospect of development of soil and ground resources requires knowledge of the natural environment and the resources it contains.
For the last few years, the country has been seeking to promote the natural resources of the soil and subsoil.
To do this, the prior knowledge of the spatial distribution of the different types of rocks is essential to establish the geological map. This map will serve as a basis for geological, mining and hydrogeological researches.
PROPOSAL OF THE COMOROS MAPPING PROJECT
The project of geological mapping of the Comoros Islands at a scale of 50,000 (1º x 1º) requires a program that will last several years and foresees to accomplish the following tasks
Mapping of all three islands (Grande-Comores, Anjouan and Mohéli) of the archipelago at a scale of 1:50,000
Airborne geophysical surveys of the whole country (if necessary)
Geochemical study of the archipelago
Identification of economically exploitable mineral substances
Training and capacity building of Comorian geologists
Creation of a litho-preparation workshop
OBJECTIVE OF THE PROGRAM
The objective of this project is the elaboration of a geological map which will be an essential tool for
Exploration, exploitation and rational management of mineral resources;
For geological and hydrogeological research.
This map can also serve as a basis for :
the elaboration of the land use plan, urban planning and the orientation of civil engineering works;
risk assessment (landslides, collapses, floods);
scientific research.